Indeed, if you are interested in the performance and longevity of your particular PC and computers, it is valuable to track your CPU temperature. But what exactly is considered a good CPU temperature? The CPU is the heart of your computer, performing most of the computational work. A low CPU temperature may reduce program performance or lead to hardware malfunction, so tracking its temperature is important.
It would help if you used high fan speeds or purchased an efficient CPU cooler to ensure the processor stays cold, performs optimally, and lasts longer.
This article will discuss an appropriate CPU temperature, why it matters, and how to maintain a cool, functional system.
What temperature range should your CPU typically operate within?
1. Idle activity: The Calm Before the Storm:
The best temperature for your CPU varies with its type, but a good resting temperature usually sits between 30°C and 50°C (86°F and 122°F). This is the lowest temperature range, as the CPU is not actively working.
2. Heavy load activity: The Heat of Action:
Ordinary temps are between 60°C and 80°C when the CPU is engaged in activities such as gaming or creating video content, among others. This is still acceptable; however, to avoid thermal throttling or damage, one must ensure that the temperature doesn’t exceed 80°C for a very long period, as nobody wants their computer to fry like a frying egg.
3. Light load activity: Gentle Hum:
Under typical usage, such as web browsing or running basic applications, a computer’s casing temperature can increase from 40°C to 60°C (104°F to 140°F). However, this is still considered as ordinary working temperature.
4. Critical Temperatures: The Danger Zone:
Every CPU has a maximum temperature threshold, often called the junction or die. The standard temperature limit for most contemporary CPUs tends to hover between 90°C and 100°C (194°F to 212°F). Any temperature above this point is hazardous to the CPU, mainly because it causes burning, which leads to instabilities in the system and eventually halts the entire system.
At what temperature can a CPU be damaged?

It’s good counsel to ensure the temperature remains below 80°C (176°F). Going beyond that can have serious consequences. So, keep it cool and play it safe! Exposure may be sustained beyond the specified limit, which could pose some difficulties. Going beyond this can lead to thermal throttling; the CPU can lower its speed to avoid further heating up.
When the temperature exceeds 80°C, it influences the CPU’s internal structures, leading to deterioration. While current-generation processors, including AMD’s Ryzen, include a thermal throttling mechanism that shuts down a processor if it reaches very high temperatures, it is still possible to degrade it unnecessarily after a few years of usage by using it at higher than recommended temperatures.
Are you worried about your CPU running too hot? It’s wise to monitor its temperature to ensure it operates in a safe zone. To track the temperature in your computer’s BIOS, a convenient tool like Core Temp could promptly help. This tool costs nothing and offers straightforward access to such crucial data.
Read More: SSIS 950-The Future of Data Integration
Factors Affecting CPU Temperature:
1. Cooling Solutions:
The cooling system you choose matters greatly for keeping your CPU temperature optimal. Air coolers, liquid cooling systems, and custom cooling setups can drastically affect how well your CPU stays cool. Investing in a high-quality cooler is sure to have an obvious effect.
2. The Environment Matters:
The room temperature where your computer is located can also impact CPU temperatures. A warmer environment can lead to higher idle and load temperatures. Ensuring proper ventilation and cooling in your workspace can help maintain lower CPU temperatures.
3. CPU Usage:
The more demanding the tasks you run, the hotter your CPU will get. Running multiple applications simultaneously or engaging in resource-intensive tasks will naturally increase CPU temperatures. Monitoring your CPU usage can help you understand how different tasks affect temperature.
4. Dust and Maintenance:
Dirt layers can block wind routes and hinder cooling efficiency. Frequent cleaning of the interiors of this device, such as the fans and heatsinks, will help minimize temperature problems. A clean system runs at a higher temperature and has better operation.
Read More: Pondershort.com-Where Thoughts Take a Dip
Monitoring and Managing CPU Temperature:
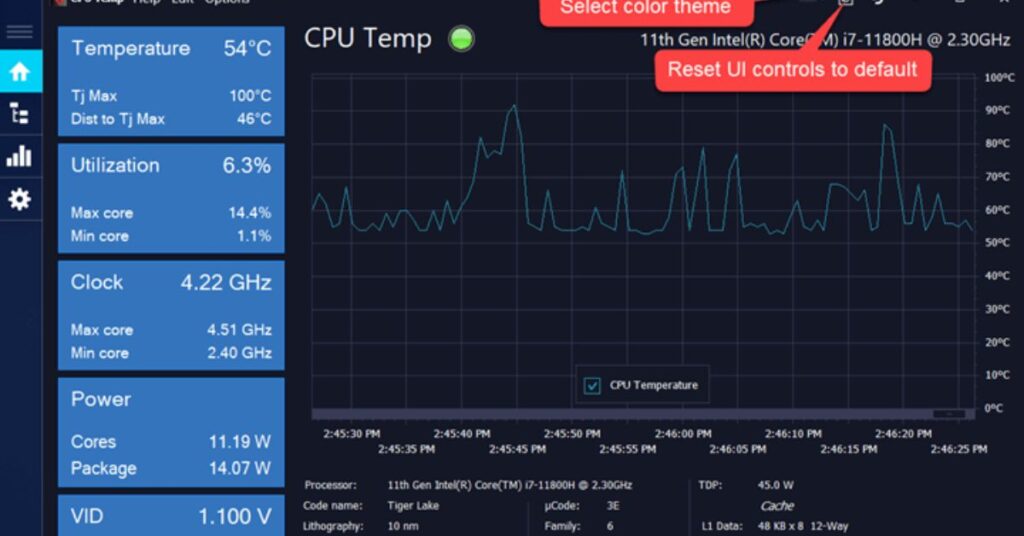
1. Software used in Monitoring Temperature:
Monitoring tools such as Core Temp, HWMonitor, and especially MSI Afterburner will assist you in monitoring the heat of your processor. You can also monitor your CPU temperatures through your computer’s bios settings. It’s like having a digital thermometer for your computer—there’s no need for a forehead scan here.
2. Effective Cooling Solutions:
Consider installing superior case fans if your CPU runs hotter than a jalapeño. Whether investing in a beefier cooler or improving your PC’s airflow, this care will keep your processor cool, which is key to a happy and healthy computer.
Read More: Carbonnen-The Revolutionary Material for Sustainable Innovation Across Industries
Tips for Maintaining Optimal CPU Temperature:
Keeping your CPU cool is vital for both performance and longevity. Here are some tips:
1. Consider purchasing a high-quality cooler:
Investing in a more effective cooling solution might be advisable if you routinely observe elevated CPU temperatures. A good CPU cooler is your premier guard against turning the heat up too much. Consider upgrading if you are using the stock cooler.
2. Ensure Proper Airflow:
Set your cables in order, use case fans, and clear out any hindrances to airflow. Proper airflow helps disseminate heat more effectively.
3. Control Ambient Temperature:
Keep your computer in a cool place where air can freely circulate. Computer in a cool, well-ventilated room. If necessary, add extra fans or a cooling pad. Regular monitoring lets you catch any potential overheating issues before they become critical.
Read More: Iamnobody89757-Where Anonymity Meets Digital Visibility
FAQs:
1. What are the consequences of having a high CPU temperature?
According to Intel, high CPU temperatures cause the computer to throttle, lessening its performance and posing a risk of damage to the processor and other components.
2. How much temperature can it reach in the CPU before it is burnt?
Normal CPU temperatures should not exceed 80 degrees Celsius or 176 degrees Fahrenheit for long periods.
3. My CPU is running too hot. What can I do?
Check your cooling system for dust buildup, ensure proper airflow, and consider upgrading to a more efficient cooler.
Final Thoughts:
In the CPU sphere, keeping things cool is vital for long-term functioning and top-notch performance. Keep it cool, dirt-free, and properly aired. Your machine will repay you with stressless running and a prolonged life. Remember, a well-maintained CPU temperature enhances your system’s performance and lifespan.
